DEPRECATED > How to install the RISC-V toolchain?
Contents |
Deprecation notice
In mid-2019, the RISC-V toolchain binaries were moved from the GNU MCU Eclipse project to the xPack project. The new install page is:
All previous releases are still available in the @gnu-mcu-eclipse scope,
but were deprecated and are not recommended for new projects.
Easy install
For RISC-V, the recommended method to install the latest version of the toolchain is:
$ xpm install --global @gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc
Overview
The Eclipse RISC-V build plug-in is highly configurable in terms of toolchain executable names and location, so you can use any 32/64-bit RISC-V GNU toolchain you prefer, but, for better results, the recommended toolchain for bare metal target applications is GNU MCU Eclipse RISC-V Embedded GCC. This toolchain closely follows the official RISC-V distribution maintained by SiFive.
Target vs host platform
Please note the distinction between the target platform and the host/development platform.
- the target platform defines the environment where the application will be executed, and in general can be either a bare metal (the application sits directly on the hardware and has intimate control of it), and applications that sit on top of an operating system, usually a distribution of GNU/Linux optimised for embedded environments
- the host/development platform is the platform where the development tools are executed, usually as cross compilers, and can be, in our case, any platform that supports Eclipse, for example Windows, macOS, GNU/Linux, etc.
Note: Be sure you select the proper toolchain for the target platform, otherwise builds will not succeed, or the generated applications will fail to run. Do not try to use the RISC-V Embedded GCC to build GNU/Linux applications, because the executables will not run on anything than bare metal, and do not try to use the Linux toolchains for bare metal applications.
The installation details described below assume the selection of the GNU MCU Eclipse RISC-V Embedded GCC toolchain. For other toolchains, please follow the specific installation instructions.
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc
After installing the toolchain, you’ll end up with lots of programs prefixed by riscv-none-embed-. For those used to the RISC-V original toolchains, there is no riscv64- or riscv32- prefix since it is actually not needed, the toolchain produces both 32/64-bit binaries, based on -march and -mabi.
Be sure you do select carefully the proper release file to match the 32/64-bit platform you are using.
The xPack install
This method uses the portable tool xpm, the xPack Package Manager, and can be used on Windows, macOS and GNU/Linux.
$ xpm install --global @gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc
This will always install the latest available version, in the central xPacks repository, which is a platform dependent folder:
- Windows:
%APPDATA%\xPacks(or%userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\xPacks,C:\Users\ilg\AppData\Roaming\xPacks) - macOS:
${HOME}/Library/xPacks - GNU/Linux:
${HOME}/opt/xPacks
This location is also known by Eclipse, so it can automatically identify the installed toolchains.
Note: This location is configurable using the environment variable
XPACKS_REPO_FOLDER; for more details please check the
xpm folders page.
The actual binaries are extracted from the distribution archive in a
folder named .content, located in the versioned xPack folder. On some
platforms, dotted files are hidden by default, so the file explorer might
require additional settings to make them visible.
Windows antivirus warning: aggressive antiviruses may prevent xpm to install binary xPacks; see FAQ
Manual install
For all platforms, the RISC-V Embedded GCC toolchain is released as a portable archive that can be installed in any location.
The archives can be downloaded from GitHub Releases.
Note: For manual installs, the recommended install location is different from the xPack install folder.
Windows
The Windows versions of RISC-V Embedded GCC are packed as .zip files. Download the latest version named like:
gnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-win64.zipgnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-win32.zip
Select the -win64 file for Windows x64 machines and the -win32 file for Windows x32 machines.
Unpack the archive and copy it into the %userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\GNU MCU Eclipse (for example C:\Users\ilg\AppData\Roaming\GNU MCU Eclipse) folder; according to Microsoft, this is the recommended location for installing user specific packages;
Note: although perfectly possible to install the toolchain in any folder, it is highly recommended to use this path, since the GNU MCU Eclipse plug-ins can automatically identify the toolchain if installed in this location.
For Windows, the next step would be to install the build tools (make & rm).
macOS
The macOS version of RISC-V Embedded GCC is packed as a .tgz archive. Download the latest version named like:
-
gnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-osx.tgz
To install the toolchain, unpack the archive and copy it to /${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/:
$ mkdir -p ${HOME}/opt
$ cd ${HOME}/opt
$ tar xf ~/Downloads/gnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-osx.tgz
$ chmod -R -w ${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/7.2.0-2-20180111-2230
Note: although perfectly possible to install the toolchain in any folder, it is highly recommended to use this path, since the GNU MCU Eclipse plug-ins can automatically identify the toolchain if installed in this location.
Test if the compiler is functional; use the actual install path:
$ ${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/7.2.0-2-20180111-2230/bin/riscv-none-embed-gcc --version
riscv-none-embed-gcc (GNU MCU Eclipse RISC-V Embedded GCC, 64-bit)
GNU/Linux
The GNU/Linux versions of RISC-V Embedded GCC are packed as .tgz archives. Download the latest version named like:
gnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-centos64.tgzgnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-centos32.tgz
As the name implies, the binaries were created on CentOS, but can be executed on most recent GNU/Linux distributions (they were tested on Debian, Ubuntu, Manjaro, SuSE and Fedora). Select the -centos64 file for 64-bit machines and the -centos32 file for 32-bit machines.
To install the toolchain, unpack the archive and copy it to /${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/:
$ mkdir -p ${HOME}/opt
$ cd ${HOME}/opt
$ tar xf ~/Downloads/gnu-mcu-eclipse-riscv-none-gcc-7.2.0-2-20180111-2230-debian64.tgz
$ chmod -R -w ${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/7.2.0-2-20180111-2230
Note: although perfectly possible to install the toolchain in any folder, it is highly recommended to use this path, since the GNU MCU Eclipse plug-ins can automatically identify the toolchain if installed in this location.
Test if the compiler is functional; use the actual install path:
$ ${HOME}/opt/gnu-mcu-eclipse/riscv-none-gcc/7.2.0-2-20180111-2230/bin/riscv-none-embed-gcc --version
riscv-none-embed-gcc (GNU MCU Eclipse RISC-V Embedded GCC, 64-bit)
Toolchain path
DO NOT add the toolchain path to the user or system path!
If there would be only one single version of one single toolchain in existence, then it wouldn’t be a problem, but as soon as you start real world applications, you will face at least the need to keep multiple versions of the same toolchain installed, if not multiple toolchains, and this is when your trouble starts.
The GNU MCU Eclipse plug-in has an advanced toolchain path management (presented in more detail in the separate page). Use it!
Select the xPack version
The recommended method for selecting the toolchain path is via the xPack… button, and selecting the xPack version.
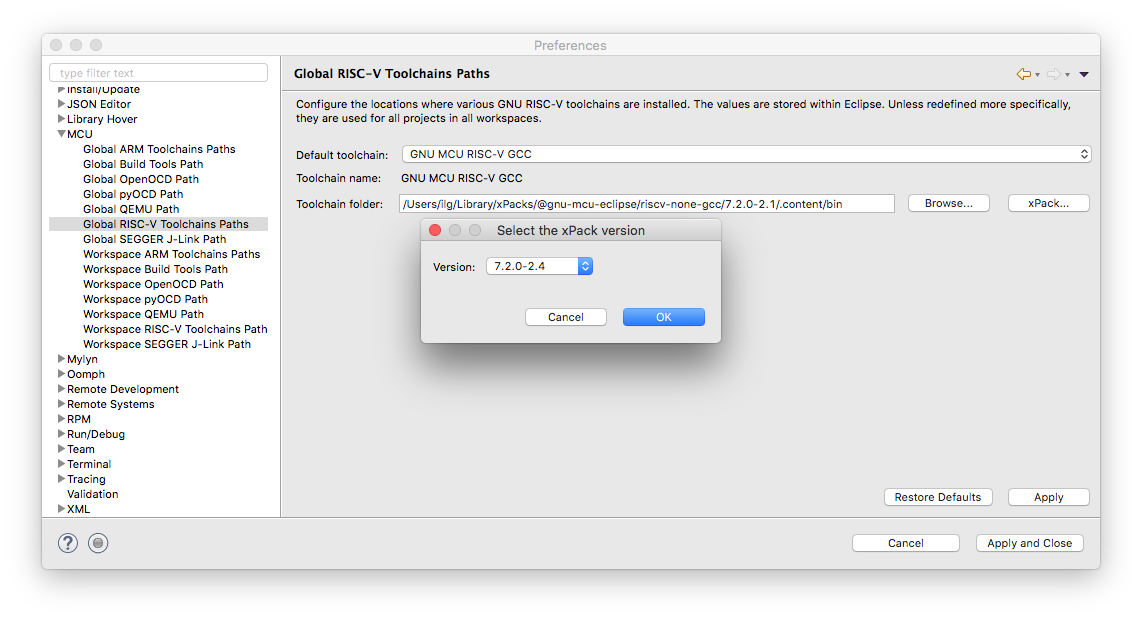
Uninstall
Should you ever need to remove the toolchain, only remove the xPack folder, there are no other components stored in any system folders.
If installed manually, remove the riscv-none-gcc/7.2.0-2-20180111-2230 folder.
Documentation
The GNU MCU Eclipse RISC-V Embedded GCC distribution includes the standard documentation, in info, man and pdf format.
The documentation is located in the share/doc folder, for example the pdf files are:
$ tree share/doc/pdf
share/doc/pdf
├── annotate.pdf
├── as.pdf
├── bfd.pdf
├── binutils.pdf
├── gcc
│ ├── cpp.pdf
│ ├── cppinternals.pdf
│ ├── gcc.pdf
│ ├── gccinstall.pdf
│ └── gccint.pdf
├── gdb.pdf
├── gprof.pdf
├── ld.pdf
├── libc.pdf
├── libiberty.pdf
├── libm.pdf
├── porting.pdf
├── refcard.pdf
└── stabs.pdf
1 directory, 18 files
